LH and FSH (Gonadotrophins)
Chemical Pathology
Notes
Synthesis and release of pituitary hormones luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is under the control of gonadotrophin releasing hormone from the hypothalamus, and modulated by circulating gonadal steroids. These tests are therefore used routinely to assess the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis.
LH and FSH are indicated for the investigation/management of:-
- Fertility problems
- Menstrual irregularities (oligo/amenorrhoea in younger women)
- Suspected pituitary gland disorders
- Delayed or precocious puberty
LH and FSH are NOT routinely recommended for diagnosing menopause. The diagnosis in women over 45 years of age with typical menopause symptoms is clinical. Further investigation is only warranted if there are any atypical symptoms.
- FSH is of no value in women taking combined oestrogen and progestogen contraception or high dose progestogen.
- In women younger than 45 years, FSH levels may be helpful if premature menopause is suspected. If not on hormonal contraception then raised FSH levels in 2 bloods samples collected 4-6 weeks apart support the diagnosis (refer to NICE guideline [NG23] Menopause: diagnosis and management.
LH:FSH ratios are often raised (>2.5) in samples collected days 1-5 of the menstrual cycle in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOs) but can be normal. The diagnosis can be made if 2 out of 3 of the following criteria hold and other causes of menstrual disturbance and hyperandrogenisation have been excluded:
- Infrequent or anovulation (usually shows as infrequent or no menstruation)
- Clinical or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenisation (check testosterone + SHBG)
- Polycystic ovaries on ultrasonography
Sample requirements
- If patient on high dose biotin therapy (>5mg/day) collect sample at least 8 hours after the last dose.
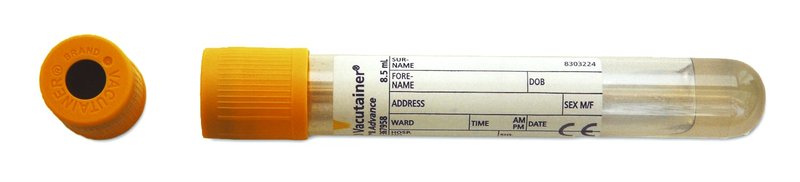
For adults, blood taken into a 5mL gold top gel tube (or rust top for the Acute Unit)
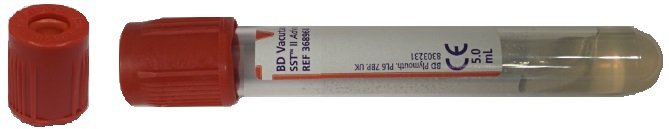
For children, blood taken into a 3.5mL rust top tube
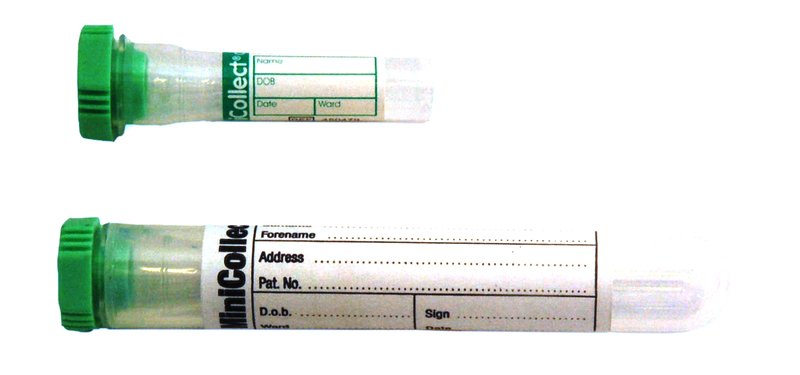
For neonates, blood taken into a 0.8mL minicollect lithium heparin tube
Please list the tests of particular interest so that some priority can be given to analysis if plasma volumes are small.
Storage/transport
Send at ambient temperature to the laboratory, If unavoidable, samples can be stored refrigerated overnight.
Required information
Include relevant clinical details, including day of cycle, menstrual history, fertility problems, any signs of hyperandrogenisation or virilisation (rate of onset of this is significant), hypogonadism, suspected pituitary problem.
Turnaround times
The assays are run throughout the day and night. The in-lab turnaround time is less than 24 hours.
Reference ranges
| Gender/Age | Phase of cycle | LH (IU/L) | FSH (IU/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adult female | Follicular phase | 1 – 12 | 1 – 9 |
| Ovulatory phase | 16 – 104 | 6 – 26 | |
| Luteal phase | 1 – 12 | 1 – 9 | |
| Post-menopausal | 16 – 66 | 30 – 118 | |
| Adult male | 1 – 8 | 1 – 7 | |
| Pre-pubertal | |||
| < 6 months old | 1 – 10* | 1 – 4* | |
| 6 months – 10 years old | <1 – 5* | <1 – 3* |
*Interpretation of LH and FSH results in children should be discussed with a Paediatric Endocrinologist
LH levels are reported as IU/L using the 2nd International Standard (NIBSC) 80/552.
FSH levels are reported as IU/L using the 2nd IRP WHO reference standard 78/549.